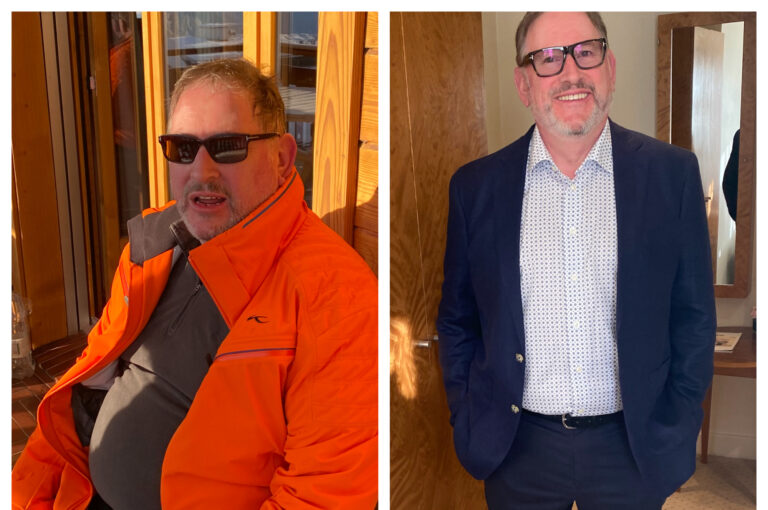
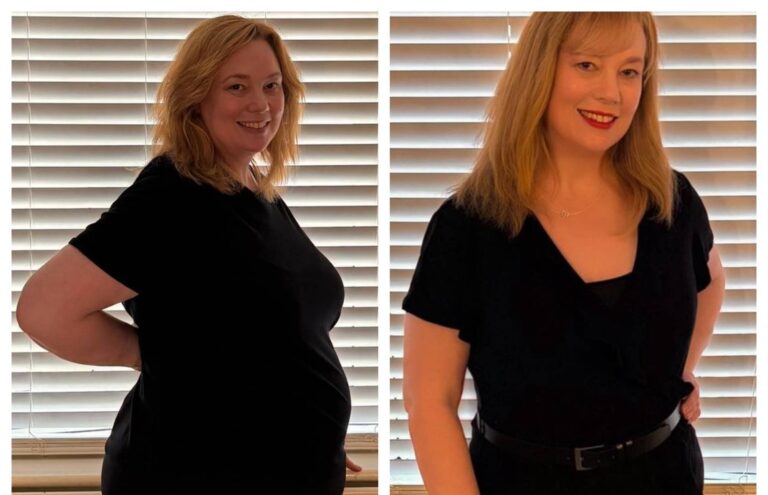
It’s now 2026 and as we know, millions of people have lost weight thanks to weight loss drugs. Despite the benefits, GLP-1 treatments are not without risks and side effects, and it’s essential to go in with your eyes open and be aware of potential side effects:
What are GLP-1 treatments, and how do they work?
GLP-1 receptor agonists are treatments designed to aid weight loss by mimicking the GLP-1 hormone, which helps regulate appetite. These medications work by slowing digestion, reducing hunger signals, and promoting a feeling of fullness, leading to lower calorie intake. Remember: these are prescription medications and you must meet the criteria – for more info read our article on the UK prescription rules and process.
Proven benefits of GLP-1 weight loss drugs
Clinical studies have shown that weight loss treatments can deliver significant results. For example, clinical trials of Mounjaro (tirzepatide) reported an average weight loss ranging from 16.0% to 22.5% of body weight (Eli Lilly, 2022), while Wegovy (semaglutide) studies showed an average reduction of 15-18% depending on study parameters and adherence to treatment (Novo Nordisk, 2021). Results may vary depending on dosage, lifestyle changes, and adherence to treatment plans.
Key benefits include:
- Significant weight loss – Many users experience steady reductions in body weight over several months, particularly when treatments are combined with healthier eating habits and increased physical activity.
- Improved eating habits – These treatments can reduce cravings and emotional eating, helping users develop healthier relationships with food.
- Sustainable changes – Because GLP-1 treatments help manage hunger, they may make it easier to maintain weight loss over time when paired with lifestyle changes.
Are GLP-1 weight loss drugs safe?
- Mild Side Effects – Nausea is one of the most commonly reported issues, affecting approximately 44% of users during treatment. Vomiting occurs in around 30%, and diarrhoea is experienced by about 21% of users, especially during the initial phases. These symptoms often improve over time as the body adjusts to the medication (Verywell Health, 2024).
- Loss of muscle mass — Some users experience loss of muscle mass along with fat loss, particularly if weight loss occurs. This may lead to weakness, reduced strength, and slower metabolism. Incorporating strength training and sufficient protein intake can help minimise this effect. Consult your doctor or a dietitian to create a balanced plan.
- More serious risks — Pancreatitis has been associated with GLP-1 treatments, and patients should be alert to symptoms such as persistent, severe abdominal pain. Treatment should be discontinued, and a healthcare provider should be consulted if pancreatitis is suspected. GLP-1 treatments may also lead to gastrointestinal complications, including gallbladder-related issues. While these risks are considered rare, they should be taken seriously (NHS Barnsley CCG Guidelines, 2024).
- Long-term safety — As these treatments are relatively new for weight management, research into their long-term safety is ongoing. Users should stay informed and regularly consult their doctors.
Who should avoid GLP-1 treatments?
GLP-1 treatments may not be suitable for everyone. People with the following conditions should discuss their options with their doctor or healthcare provider:
- A history of pancreatitis
- Thyroid cancer or a family history of thyroid tumours
- Severe gastrointestinal conditions
If you have any concerns about whether GLP-1 treatments are appropriate for you, it is essential to consult your doctor before starting treatment.
Making an informed decision

Starting GLP-1 treatment is a significant step, and as we’ve said, it’s important to make an informed choice. Here are some key actions to help:
- Consult your doctor or healthcare provider — Discuss your weight-loss goals and discuss your medical history and current health conditions.
- Set realistic goals — GLP-1 treatments are most effective when combined with healthy eating and regular exercise. They are not quick fixes but tools to support sustainable weight loss.
- Track progress and symptoms — Monitor your weight loss and note any side effects. Regular check-ins with your healthcare provider can help address concerns and make adjustments as needed.
- Stay informed — Ask questions about risks, alternatives, and long-term expectations. Your doctor can guide you through the decision-making process.
Managing side effects and staying on track
Side effects can be one of the biggest concerns for people considering GLP-1 treatments. Practical steps to manage side effects include:
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals — Eating smaller portions and spacing meals throughout the day can help reduce nausea and vomiting, particularly during the first few weeks of treatment.
- Stay hydrated — Drinking water regularly can prevent dehydration caused by diarrhoea, especially if symptoms persist for several days.
- Adjust dosage gradually — Gradually increasing the dosage, as recommended by healthcare providers, has been shown to lower the risk of nausea and gastrointestinal discomfort (Verywell Health, 2024).
- Incorporate strength training — To minimise muscle loss, include resistance exercises and ensure adequate protein intake.
If side effects persist or worsen, it is important to contact your healthcare provider immediately to discuss adjustments or alternatives.
Final thoughts
GLP-1 treatments offer a promising option for weight loss, especially for those who have struggled with traditional diet and exercise approaches. However, they are not a one-size-fits-all solution. While these treatments can do much of the heavy lifting, they work best when paired with sustainable lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet and regular physical activity (we know you’ve heard it a 1000 times, but it’s true, and sometimes more manageable than you think). By carefully weighing the benefits and risks, asking the right questions, and working closely with a healthcare provider, readers can make informed decisions about whether these treatments are the right choice. And as always, all the best on your weight loss journey.